
Why These BIM Features Are Crucial for AEC Success
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has become a game-changer in the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) industry. By allowing professionals to create detailed digital models of projects, BIM goes beyond traditional blueprints. It supports every phase of the project lifecycle, from planning and design to construction and facility management. BIM’s real power lies in its ability to bring teams together, improving collaboration and reducing costly mistakes. This blog will explore the essential features of BIM that are shaping today’s projects. We’ll cover capabilities like 3D modeling, clash detection, and real-time updates, which help AEC professionals work smarter and more efficiently. From sustainability analysis to project coordination, these BIM tools and processes drive better results, reduce risks, and support smooth project execution. Understanding these key BIM features can give teams a real edge in today’s competitive AEC landscape.
1. Advanced 3D Modeling and Visualization
One of BIM’s standout capabilities is its advanced 3D modeling and visualization. With BIM, teams can create highly detailed, realistic digital models that go far beyond traditional 2D drawings. These 3D models offer a comprehensive view of the project, allowing architects, engineers, and contractors to see exactly how each element fits together. This level of detail improves design accuracy, helping teams spot potential issues early, before they become costly errors in construction. For example, a project team might notice a structural clash between HVAC ducts and plumbing lines during the modeling phase. Identifying this flaw early prevents expensive adjustments and delays down the line.
3D visualization also enhances stakeholder communication. It allows project managers to present realistic images of the design, making it easier for clients and other stakeholders to understand the vision. Instead of trying to interpret complex blueprints, stakeholders can see a clear, visual representation of the final project. This transparency fosters confidence and reduces the chances of misunderstandings. Advanced 3D modeling in BIM brings the design to life, making collaboration smoother and ensuring everyone is on the same page from start to finish.
2. Enhanced Collaboration and Coordination
BIM is a powerful tool for enhancing collaboration and coordination in the AEC industry. It acts as a central hub where architects, engineers, contractors, and other stakeholders can share real-time information, helping everyone stay aligned. By having a single, updated model, all team members can access the latest project details and avoid the confusion caused by outdated information. This centralized approach reduces miscommunications and ensures that each team’s work complements the others, preventing costly rework and delays.

For instance, in a large office construction project, BIM enabled seamless coordination among the design, structural, and mechanical teams. With real-time updates, each team was alerted to any design changes immediately, allowing them to adjust their plans on the go. This prevented schedule disruptions and kept the project moving forward smoothly. By using BIM for collaboration, the project stayed on track and was completed on time, saving both time and resources. This capability makes BIM an invaluable tool for complex projects where effective communication is essential to success.
3. Clash Detection and Conflict Resolution
Clash detection is one of BIM’s most valuable features, allowing teams to identify and resolve design conflicts before construction starts. BIM's advanced modeling technology brings together all building elements—structural, electrical, plumbing, and mechanical—into a single model, making it easy to spot clashes that could disrupt construction. By addressing these issues during the design phase, teams can avoid costly on-site changes, save time, and prevent project delays.
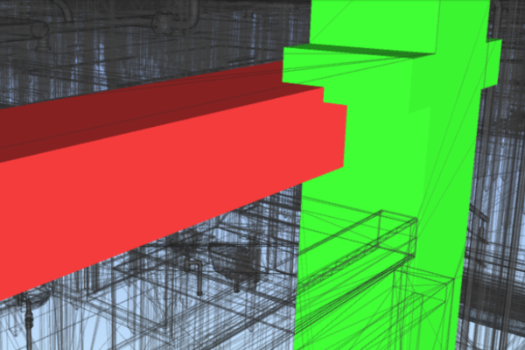
For example, on a hospital construction project, BIM’s clash detection uncovered a critical conflict between the HVAC ductwork and a main structural beam. Without BIM, this clash might not have been found until installation, which would have led to time-consuming adjustments and potential damage to the schedule. By spotting the problem early, the team was able to re-route the ductwork in the design phase, avoiding structural issues and maintaining harmony between systems. This proactive approach ensures that all building elements work together as intended, creating a smoother construction process and a more efficient final structure. Through clash detection, BIM helps keep projects on track and within budget by addressing issues before they become costly obstacles.
4. Comprehensive Lifecycle Management
BIM is more than just a tool for design and construction; it supports the entire lifecycle of a building, from initial concept to long-term maintenance. With BIM, facility managers have access to a wealth of data about the building's systems, materials, and layout, all stored in one place. This centralized information makes it easier to manage ongoing maintenance and ensures that teams have detailed, accurate data at their fingertips when issues arise.
For example, imagine a commercial office building where HVAC maintenance is a recurring need. With BIM, the facility manager can quickly pull up detailed information on the system, including part specifications, maintenance history, and installation details. This level of detail not only simplifies regular upkeep but also helps the manager identify efficient solutions when repairs are needed, saving time and reducing costs. Additionally, when it’s time to expand or renovate, BIM provides precise data on existing conditions, allowing architects and engineers to plan changes without guesswork. By supporting maintenance and future upgrades, BIM ensures that the building remains efficient and adaptable long after the initial construction is complete, proving invaluable for long-term asset management.

5. Efficient Document Management
BIM excels at organizing and managing project documents, making it a vital tool for efficient documentation. Instead of dealing with scattered files and manual handling, BIM centralizes all project documents, keeping everything easily accessible and up to date. This organized approach reduces the chances of errors that often occur with traditional document handling and ensures all team members are working with the latest information.
For instance, in a large commercial construction project, the use of BIM's document management capabilities helped the team streamline the approval process. With all required documents, drawings, and specifications stored in a single platform, project managers could quickly retrieve and share the necessary files with regulatory agencies. This seamless access helped the team secure timely approvals, avoiding delays and ensuring that all documentation met industry standards. By simplifying document management, BIM keeps projects compliant and running smoothly, saving time and preventing costly errors.
6. Sustainability and Energy Analysis
BIM is a powerful tool for promoting sustainability in building design, primarily through its energy performance analysis capabilities. By simulating energy use and efficiency during the design phase, BIM helps architects and engineers create buildings that consume less energy and have a smaller environmental impact. This analysis can guide decisions on materials, insulation, and building orientation to enhance energy efficiency right from the start.

For example, a university campus project used BIM for detailed energy modeling. By testing different HVAC systems and insulation options in the digital model, the team identified an approach that would significantly lower energy consumption. As a result, the campus achieved reduced operational costs while meeting green building certification requirements. This kind of sustainable planning helps not only to save on energy expenses but also to align projects with environmental standards. With BIM, teams can design smarter, more sustainable buildings that benefit both owners and the environment.
Conclusion
BIM offers a suite of capabilities that transform the AEC industry, from advanced 3D modeling and clash detection to efficient document management and sustainability analysis. These features improve project accuracy, streamline collaboration, and support long-term building management. By leveraging BIM, AEC professionals can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and meet modern sustainability standards. Now is the time to explore BIM’s potential for your projects. Embracing these tools can give you a competitive edge in an industry that’s rapidly evolving. Discover how BIM can make a difference in your next project, ensuring success from start to finish.